Incomplete Bladder Emptying: Causes and Treatments
Do you experience the urge to urinate many times during the day and still your bladder feels full? Do you experience bladder leakage? Do you have trouble starting to urinate or experience an inability to urinate? If these symptoms sound familiar, you may be experiencing incomplete bladder emptying. This is also known as urinary retention.
Urinary retention affects people with penises and vaginas. It is the most common urological complaint in emergency departments.
Urinary retention most often impacts people over age 50.
Vaginal birth, certain medications, and muscle dysfunction can contribute to urinary retention. Obstructions of the urethra are another likely cause of residual urine.
If you think you may be suffering from urinary retention, talk to a urogynecologist who can help. Keep reading to learn more about the possible causes and treatments.
How Does the Bladder Function?
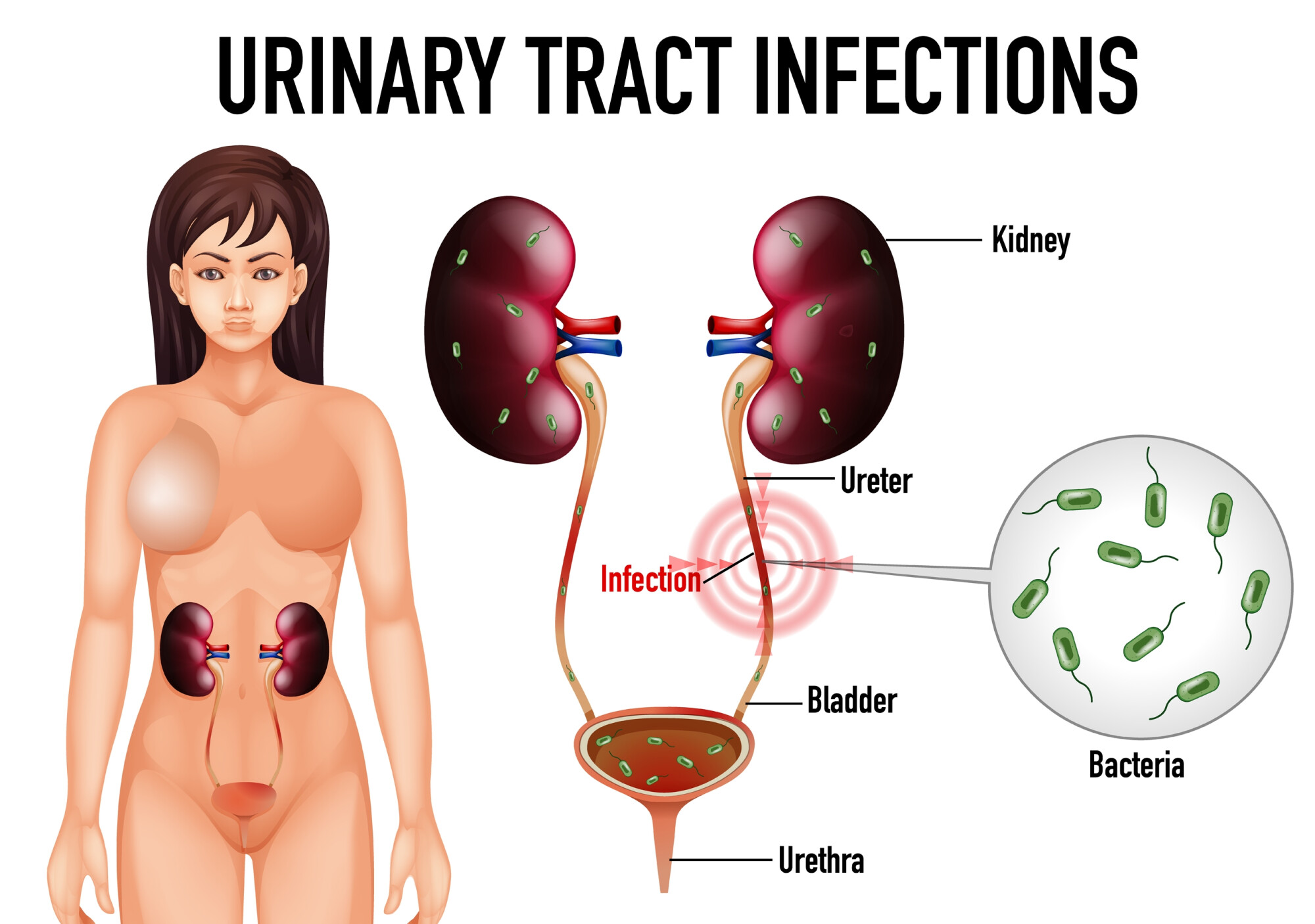
The urinary bladder has two jobs. It stores urine and drains it. Sounds simple, but the urinary bladder is a more complex organ than your might think.
Here’s how it works. There are two circular muscles that surround and enclose the urethra. These are called sphincters.
To empty the bladder, the sphincter muscles and the bladder muscles need to work together. First the sphincter muscles open and then the bladder contracts to empty the urine.
When the bladder is healthy and functioning properly, the urinary bladder empties completely. There should not be excessive pressure, nor should any urine remain in the bladder.
An intact nervous system is also important for proper bladder functioning.
The brain sends send the signal to urinate through the nervous system. These signals allow the sphincter and bladder muscles to coordinate.
The Importance of Pelvic Floor Health
Awareness of the importance of pelvic floor health has grown over the past few years. And pelvic floor therapy has gained increasing popularity – for good reason.
For people with vaginas, pelvic floor muscles are very important. They are responsible for keeping the bladder, vagina, uterus, and rectum in place.
During pregnancy, pelvic floor muscles help support the baby. They’re also integral to the birthing process.
If you are experiencing pelvic floor problems, talk to a doctor. A urogynecologist can offer expertise beyond the scope of a primary care physician.
Consulting a urogynecologist can have a significant positive impact on pelvic floor health.
What Is Urinary Retention?
Urinary retention occurs when the bladder is unable to empty completely. This results in residual urine left in the bladder and can cause health complications.
While some people with urinary retention are able to pass some urine, others experience an inability to urinate. Even those who do pass some urine experience incomplete bladder emptying.
Why Is Residual Urine Bad for Your Health?
When residual urine is left in the bladder, germs can build up on the inner walls of the organ. This is because the bladder cannot rinse, which can lead to infection and the formation of urinary stones.
If left untreated for a long period of time, residual urine and bladder retention can cause chronic kidney damage. Urinary retention can be very painful and cause over-expansion of the bladder.
If you are experiencing incomplete bladder emptying it is best that you see a urogynecologist as soon as possible.
What Causes Incomplete Bladder Emptying?
There are many causes of urinary retention in people with vaginas. These causes can range from urethral and urinary bladder diseases to pelvic floor fractures to uterine prolapse.
Neurogenic causes such as stroke and multiple sclerosis can also cause urinary retention.
However, the most common causes of incomplete bladder emptying are divided into two categories. These categories are acute urinary retention and chronic urinary retention.
Acute Urinary Retention
Acute urinary retention is the sudden inability to urinate. Typically it’s a symptom of an underlying bladder or urethra problem. People with urinary retention experience a painful need to urinate and distended abdomens.
The causes of acute urinary retention include bladder blockage and urethral blockage. It can also result from nervous system disruption or an overstretched bladder.
Chronic Urinary Retention
Chronic urinary retention is similar to acute retention but occurs over a long period of time. It is often caused by bladder obstructions, weakened bladder muscles, or neurological problems.
Chronic urinary retention can also be a side effect of medication.
Chronic urinary retention can be confusing. Sometimes you may be able to urinate.
However, when you do urinate, you may experience difficulty starting a stream.
People with chronic urinary retention experience incomplete bladder emptying when they urinate. They urinate frequently, feel an urgent need to void their bladders, and feel they need to go again right after finishing.
Incontinence is also a symptom of chronic urinary retention
Urinary Retention Treatments & Solutions
Both chronic and acute urinary retention require treatment. These treatments range from urethral catheters to behavioral modifications to urethral dilation.
Urethral Catheter
There are two types of catheterization used to treat urinary retention. These are intermittent catheterization and indwelling catheterization.
Intermittent catheterization involves the use of a single-use urinary catheter. It is a safe and effective method for regularly emptying the bladder.
When intermittent catheterization is not effective, an indwelling urethral catheter may be necessary. This is an invasive procedure that requires placing the catheter through the abdominal wall or urethra.
An indwelling catheter empties the bladder continuously.
Urethral Dilation
Urethral dilation is useful for treating urethral stricture. Urethral stricture contributes to urinary retention. It causes the urethra to narrow and become obstructed.
Dilation of the urethra occurs by inserting tubes into the urethra. The tubes grow wider to relieve the stricture and open the urethra.
Another form of urethral dilation involves inserting a catheter into the urethra. On the end of the catheter is a small balloon. Once inside the urethra, the balloon inflates to open the blockage.
All types of urethral dilation use local or general anesthesia to avoid discomfort.
Urethral Stent
Another way to treat urinary retention is to insert a stent (tube) into the urethra. When the stent is in place, it expands to widen the urethra.
A stent can be either permanent or temporary.
Talking to a Urogynecologist Can Help
Incomplete bladder emptying is a painful and limiting condition that requires treatment. Without treatment, urinary retention can lead to infection, obstruction, and chronic kidney damage.
The best option is to consult a urogynecologist. Urogynecologists specialize in obstetrics and gynecology. They focus on pelvic health and have more specific expertise in this area than primary care physicians.
Contact Peter M. Lotze, MD, a trusted Houston urogynecologist today.

MichaelAlcob
“I must thank you for the efforts you have put in writing this blog. I’m hoping to see the same high-grade blog posts by you in the future as well. In truth, your creative writing abilities has encouraged me to get my own blog now ;)”
http://www.linkagogo.com/go/To?url=112997179
Mark
Thanks for your blog, nice to read. Do not stop.
Christina Rhodius
The information read is very informative and will enable me to discuss this discomfort with a urogynecologist. Will seek help in a location in my area.
Peter Lotze
Thank you for your feedback. We aim to help people get the care they need, either with us or another health care provider, and we are glad you found our post beneficial. We do offer virtual visit appointments if you would like to discuss your history/symptoms and get an opinion on where to start. Contact our office directly by phone or by filling out the appointment request form on the “contact us” page if you are interested in scheduling an appointment. If not, we hope you get the care you need and control/improvement of your symptoms! Check back often for more information on urogynecology-related conditions and general health and wellness topics.
rama
I think this is an informative post and it is very useful and knowledgeable. therefore, I would like to thank you for the efforts you have made in writing this article.